Structural characterization of gallium fluoride phosphate glasses by advanced solid-state NMR methods and correlation with photophysical properties.
GADDAM, Anuraag; GALLEANI, Gustavo; REIS, Vitor de Lima; DE CAMARGO, Andrea Simone Stucchi; ECKERT, Hellmut.
GADDAM, Anuraag; GALLEANI, Gustavo; REIS, Vitor de Lima; DE CAMARGO, Andrea Simone Stucchi; ECKERT, Hellmut.




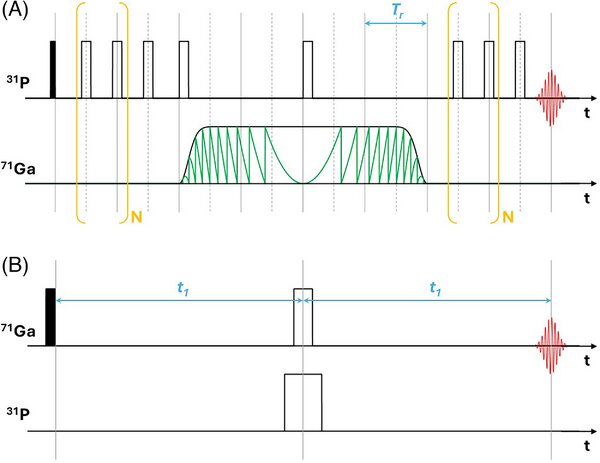 Abstract: Gallium fluoride phosphate glasses feature low refractive index, high energy radiation resistance, wide transmission range, and favorable emission characteristics of rare-earth dopants. For the development of optimized glass compositions, a fundamental understanding of these properties in terms of glass structure is sought. We report nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) structural studies of glasses in the system xGa(PO3)3-(40 - x)GaF3-20BaF2-20ZnF2-20SrF2 (x = 5, 10, 15, 20, and 25 mol%). 31P NMR results with 71Ga recoupling show that the network structure is dominated by P-O-Ga linkages, and no P-O-P linkages exist. 71Ga NMR results show that Ga is mainly six-coordinated featuring a mixed fluoride/phosphate coordination. Quantitative estimates of this ligand distribution around gallium were obtained by 71Ga{31P} spin echo double resonance (REDOR) measurements. Photophysical properties suggest changes in the Eu(III) ligand distribution toward a fluoride-dominated environment at low P/F ratio while the glass network is largely sustained by bridging oxygen atoms via P-O-Ga linkages.
Abstract: Gallium fluoride phosphate glasses feature low refractive index, high energy radiation resistance, wide transmission range, and favorable emission characteristics of rare-earth dopants. For the development of optimized glass compositions, a fundamental understanding of these properties in terms of glass structure is sought. We report nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) structural studies of glasses in the system xGa(PO3)3-(40 - x)GaF3-20BaF2-20ZnF2-20SrF2 (x = 5, 10, 15, 20, and 25 mol%). 31P NMR results with 71Ga recoupling show that the network structure is dominated by P-O-Ga linkages, and no P-O-P linkages exist. 71Ga NMR results show that Ga is mainly six-coordinated featuring a mixed fluoride/phosphate coordination. Quantitative estimates of this ligand distribution around gallium were obtained by 71Ga{31P} spin echo double resonance (REDOR) measurements. Photophysical properties suggest changes in the Eu(III) ligand distribution toward a fluoride-dominated environment at low P/F ratio while the glass network is largely sustained by bridging oxygen atoms via P-O-Ga linkages. @article={003218846,author = {GADDAM, Anuraag; GALLEANI, Gustavo; REIS, Vitor de Lima; DE CAMARGO, Andrea Simone Stucchi; ECKERT, Hellmut.},title={Structural characterization of gallium fluoride phosphate glasses by advanced solid-state NMR methods and correlation with photophysical properties},journal={Journal of the American Ceramic Society},note={v. 107, n. 12, p. 8624-8637},year={2024}}
@article={003218846,author = {GADDAM, Anuraag; GALLEANI, Gustavo; REIS, Vitor de Lima; DE CAMARGO, Andrea Simone Stucchi; ECKERT, Hellmut.},title={Structural characterization of gallium fluoride phosphate glasses by advanced solid-state NMR methods and correlation with photophysical properties},journal={Journal of the American Ceramic Society},note={v. 107, n. 12, p. 8624-8637},year={2024}}