Modification of bacterial cellulose membrane with 1,4- Bis(triethoxysilyl)benzene: a thorough physical-chemical characterization study.
MONTEIRO, Andreia S.; OLIVEIRA JUNIOR, Marcos de; SANTAGNELI, Silvia; CARCEL, Carole; GUTMANN, Torsten; BUNTKOWSKY, Gerd; MAN, Michel Wong Chi; BARUD, Hernane S.; RIBEIRO, Sidney J. L.
MONTEIRO, Andreia S.; OLIVEIRA JUNIOR, Marcos de; SANTAGNELI, Silvia; CARCEL, Carole; GUTMANN, Torsten; BUNTKOWSKY, Gerd; MAN, Michel Wong Chi; BARUD, Hernane S.; RIBEIRO, Sidney J. L.




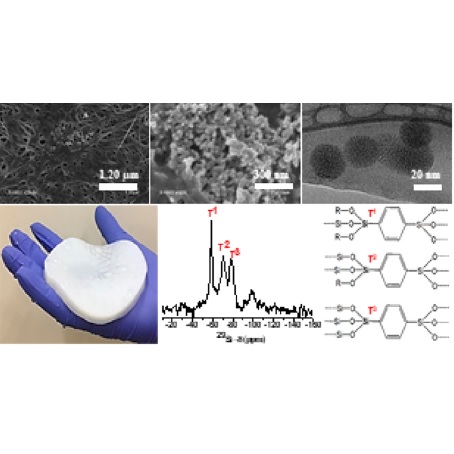 Abstract: Bacterial cellulose (BC) combined with organobridged porous silica nanoparticles offers potential opportunities to develop smart hybrid materials such as advanced drug delivery nanosystems. This work reports the preparation of bacterial cellulose membrane (BCM) and their modification by in situ methodology with the organo-bridged precursor 1,4-bis- (triethoxysilyl)benzene (BTEB). BTEB was successfully incorporated into the BCM, and spherical hybrid silica nanoparticles with heterogeneous particle size (30-100 nm) and probably porous structure were formed and characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared-attenuated total reflectance (FTIRATR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and solid state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). We further combined solid-state NMR with dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) to achieve sensitivity enhancement and to selectively enhance the NMR signal of the hydrophobic BTEB moieties on the BCM surface. This allowed us to get more detailed structural information about the BTEB-BCM multicomponent material.
Abstract: Bacterial cellulose (BC) combined with organobridged porous silica nanoparticles offers potential opportunities to develop smart hybrid materials such as advanced drug delivery nanosystems. This work reports the preparation of bacterial cellulose membrane (BCM) and their modification by in situ methodology with the organo-bridged precursor 1,4-bis- (triethoxysilyl)benzene (BTEB). BTEB was successfully incorporated into the BCM, and spherical hybrid silica nanoparticles with heterogeneous particle size (30-100 nm) and probably porous structure were formed and characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared-attenuated total reflectance (FTIRATR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and solid state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). We further combined solid-state NMR with dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) to achieve sensitivity enhancement and to selectively enhance the NMR signal of the hydrophobic BTEB moieties on the BCM surface. This allowed us to get more detailed structural information about the BTEB-BCM multicomponent material. @article={003022383,author = {MONTEIRO, Andreia S.; OLIVEIRA JUNIOR, Marcos de; SANTAGNELI, Silvia; CARCEL, Carole; GUTMANN, Torsten; BUNTKOWSKY, Gerd; MAN, Michel Wong Chi; BARUD, Hernane S.; RIBEIRO, Sidney J. L.},title={Modification of bacterial cellulose membrane with 1,4- Bis(triethoxysilyl)benzene: a thorough physical-chemical characterization study},journal={Journal of Physical Chemistry C},note={v. 125, n. 8, p. 4498-4508},year={2021}}
@article={003022383,author = {MONTEIRO, Andreia S.; OLIVEIRA JUNIOR, Marcos de; SANTAGNELI, Silvia; CARCEL, Carole; GUTMANN, Torsten; BUNTKOWSKY, Gerd; MAN, Michel Wong Chi; BARUD, Hernane S.; RIBEIRO, Sidney J. L.},title={Modification of bacterial cellulose membrane with 1,4- Bis(triethoxysilyl)benzene: a thorough physical-chemical characterization study},journal={Journal of Physical Chemistry C},note={v. 125, n. 8, p. 4498-4508},year={2021}}