Turn-on fluorescence study of a highly selective acridine-based chemosensor for Zn2+ in aqueous solutions.
NUNES, Marcelo Carpes; CARLOS, Fabiane dos Santos; FUGANTI, Otávio; GALINDO, Danyellen Dheyniffer Monteiro; DE BONI, Leonardo; ABATE, Gilberto; NUNES, Fábio Souza.
NUNES, Marcelo Carpes; CARLOS, Fabiane dos Santos; FUGANTI, Otávio; GALINDO, Danyellen Dheyniffer Monteiro; DE BONI, Leonardo; ABATE, Gilberto; NUNES, Fábio Souza.




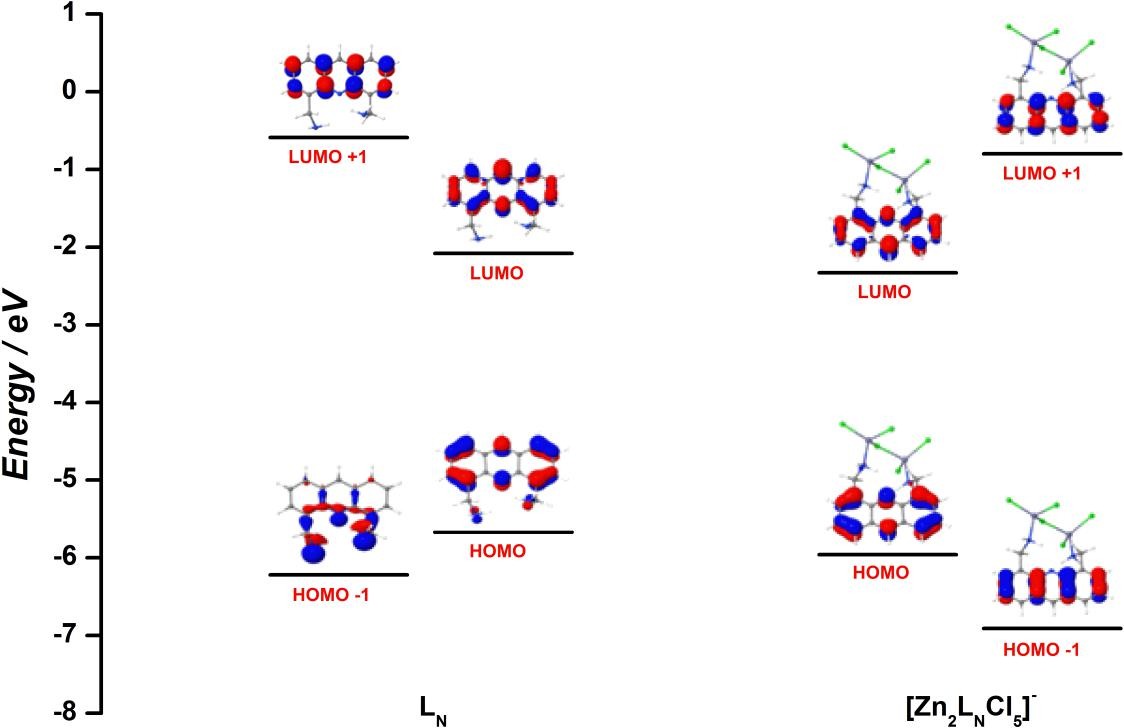 Abstract: 4,5-Bis(aminomethyl)acridine (LN) was investigated as a chemosensor for metal ions in aqueous solutions and it is selective for Zn2+, through a linear fluorescence enhancement of 230% in the concentration range of 17.8-600 µmolL-1. Benesi-Hildebrand and Job method formalisms showed the formation of a very stable complex with one of the highest binding constant (2.43×10 14 L2mol-2) reported for zinc, and a 2:1 (metal ion/sensor) ratio. DFT and TD-DFT calculations could explain the fluorescence augmentation upon complexation between Zn2+ and LN. Limit of detection and limit of quantification (R2 = 0.9970, least squares method) were found to be 5.36 and 17.8 µmol L-1, respectively, and appropriate robustness was verified based on the variation of several analytical conditions. Practical application testes showed recovery results such as (92 ± 4)% (tap water) and (99 ± 1%) (mineral water), proving to be adequate to quantify Zn2+ in real water samples, showing no effect of interfering ions.
Abstract: 4,5-Bis(aminomethyl)acridine (LN) was investigated as a chemosensor for metal ions in aqueous solutions and it is selective for Zn2+, through a linear fluorescence enhancement of 230% in the concentration range of 17.8-600 µmolL-1. Benesi-Hildebrand and Job method formalisms showed the formation of a very stable complex with one of the highest binding constant (2.43×10 14 L2mol-2) reported for zinc, and a 2:1 (metal ion/sensor) ratio. DFT and TD-DFT calculations could explain the fluorescence augmentation upon complexation between Zn2+ and LN. Limit of detection and limit of quantification (R2 = 0.9970, least squares method) were found to be 5.36 and 17.8 µmol L-1, respectively, and appropriate robustness was verified based on the variation of several analytical conditions. Practical application testes showed recovery results such as (92 ± 4)% (tap water) and (99 ± 1%) (mineral water), proving to be adequate to quantify Zn2+ in real water samples, showing no effect of interfering ions. @article={002981125,author = {NUNES, Marcelo Carpes; CARLOS, Fabiane dos Santos; FUGANTI, Otávio; GALINDO, Danyellen Dheyniffer Monteiro; DE BONI, Leonardo; ABATE, Gilberto; NUNES, Fábio Souza.},title={Turn-on fluorescence study of a highly selective acridine-based chemosensor for Zn2+ in aqueous solutions},journal={Inorganica Chimica Acta},note={v. 499, p. 119191-1-119191-9},year={2020}}
@article={002981125,author = {NUNES, Marcelo Carpes; CARLOS, Fabiane dos Santos; FUGANTI, Otávio; GALINDO, Danyellen Dheyniffer Monteiro; DE BONI, Leonardo; ABATE, Gilberto; NUNES, Fábio Souza.},title={Turn-on fluorescence study of a highly selective acridine-based chemosensor for Zn2+ in aqueous solutions},journal={Inorganica Chimica Acta},note={v. 499, p. 119191-1-119191-9},year={2020}}