Influence of different synthesis methods on the defect structure, morphology, and UV-assisted ozone sensing properties of zinc oxide nanoplates.
ORTEGA, Pedro Paulo da Silva; PALMA, João Victor Nascimento de; DOIMO, Ana Luiza de Camargo; LÍBERO, Laura Ordonho; YAMAKAWA, Gabriel Franco; MERÍZIO, Leonnam Gotardo; AGUAIR, Ederson Carlos; SILVA, Luís Fernando da; SILVA, Elson Longo da.
ORTEGA, Pedro Paulo da Silva; PALMA, João Victor Nascimento de; DOIMO, Ana Luiza de Camargo; LÍBERO, Laura Ordonho; YAMAKAWA, Gabriel Franco; MERÍZIO, Leonnam Gotardo; AGUAIR, Ederson Carlos; SILVA, Luís Fernando da; SILVA, Elson Longo da.





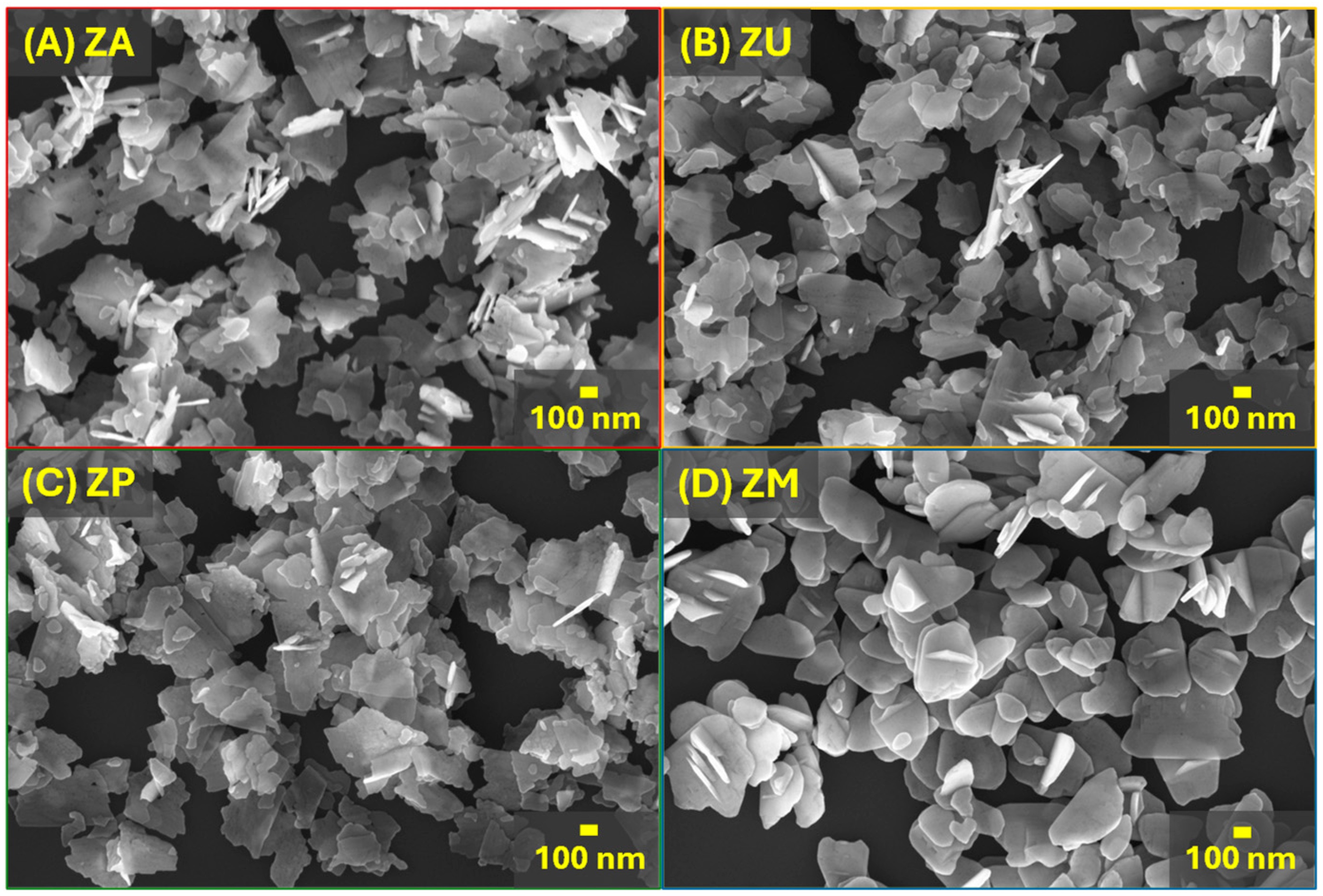 Abstract: In this work, room-temperature UV-assisted ozone detection was investigated using ZnO nanoplates synthesized via precipitation, ultrasound-, ultrasonic tip-, and microwave-assisted hydrothermal (MAH) methods. X-ray diffraction confirmed the formation of crystalline phases with an ~3.3 eV band gap, independent of the synthesis used. Raman spectroscopy revealed oxygen-related defects. Plate-like morphologies were observed, with the ultrasonic tip-assisted synthesis yielding ~17 nm-thick plates. Electrical measurements showed 10-170 ppb ozone sensitivity under UV. The sample synthesized via the MAH method (ZM) demonstrated superior conductance, with a baseline resistance of ~1.2% for the ultrasound (ZU) sample and less than 50% for the precipitation (ZA) and ultrasonic tip (ZP) samples. Despite the appreciable response in dark mode, the recovery was slow (>>30 min), except for the UV illumination condition, which reduced the recovery response to ~2 min. With top areas of ~0.0122 µm2, ZP and ZU showed high specific surface areas (24.75 and 19.37 m2/g, respectively), in contrast to ZM, which exhibited the lowest value (15.32 m2/g) with a top area of ~0.0332 µm2 and a thickness of 26.0 nm. The superior performance of ZM was attributed to the larger nanoplate sizes and the lower baseline resistance. The ultrasound method showed the lowest sensitivity due to the higher resistance and the depletion layer effect. The results indicate that the synthesis methods presented herein for the production of reactive ZnO nanoplates using NaOH as a growth-directing agent are reliable, simple, and cost-effective, in addition to being capable of detecting ozone with high sensitivity and reproducibility at concentrations as low as 10 ppb.
Abstract: In this work, room-temperature UV-assisted ozone detection was investigated using ZnO nanoplates synthesized via precipitation, ultrasound-, ultrasonic tip-, and microwave-assisted hydrothermal (MAH) methods. X-ray diffraction confirmed the formation of crystalline phases with an ~3.3 eV band gap, independent of the synthesis used. Raman spectroscopy revealed oxygen-related defects. Plate-like morphologies were observed, with the ultrasonic tip-assisted synthesis yielding ~17 nm-thick plates. Electrical measurements showed 10-170 ppb ozone sensitivity under UV. The sample synthesized via the MAH method (ZM) demonstrated superior conductance, with a baseline resistance of ~1.2% for the ultrasound (ZU) sample and less than 50% for the precipitation (ZA) and ultrasonic tip (ZP) samples. Despite the appreciable response in dark mode, the recovery was slow (>>30 min), except for the UV illumination condition, which reduced the recovery response to ~2 min. With top areas of ~0.0122 µm2, ZP and ZU showed high specific surface areas (24.75 and 19.37 m2/g, respectively), in contrast to ZM, which exhibited the lowest value (15.32 m2/g) with a top area of ~0.0332 µm2 and a thickness of 26.0 nm. The superior performance of ZM was attributed to the larger nanoplate sizes and the lower baseline resistance. The ultrasound method showed the lowest sensitivity due to the higher resistance and the depletion layer effect. The results indicate that the synthesis methods presented herein for the production of reactive ZnO nanoplates using NaOH as a growth-directing agent are reliable, simple, and cost-effective, in addition to being capable of detecting ozone with high sensitivity and reproducibility at concentrations as low as 10 ppb. @article={003246772,author = {ORTEGA, Pedro Paulo da Silva; PALMA, João Victor Nascimento de; DOIMO, Ana Luiza de Camargo; LÍBERO, Laura Ordonho; YAMAKAWA, Gabriel Franco; MERÍZIO, Leonnam Gotardo; AGUAIR, Ederson Carlos; SILVA, Luís Fernando da; SILVA, Elson Longo da.},title={Influence of different synthesis methods on the defect structure, morphology, and UV-assisted ozone sensing properties of zinc oxide nanoplates},journal={Chemosensors},note={v. 13, n. 4, p. 152-1-152-20 + supplementary materials},year={2025}}
@article={003246772,author = {ORTEGA, Pedro Paulo da Silva; PALMA, João Victor Nascimento de; DOIMO, Ana Luiza de Camargo; LÍBERO, Laura Ordonho; YAMAKAWA, Gabriel Franco; MERÍZIO, Leonnam Gotardo; AGUAIR, Ederson Carlos; SILVA, Luís Fernando da; SILVA, Elson Longo da.},title={Influence of different synthesis methods on the defect structure, morphology, and UV-assisted ozone sensing properties of zinc oxide nanoplates},journal={Chemosensors},note={v. 13, n. 4, p. 152-1-152-20 + supplementary materials},year={2025}}