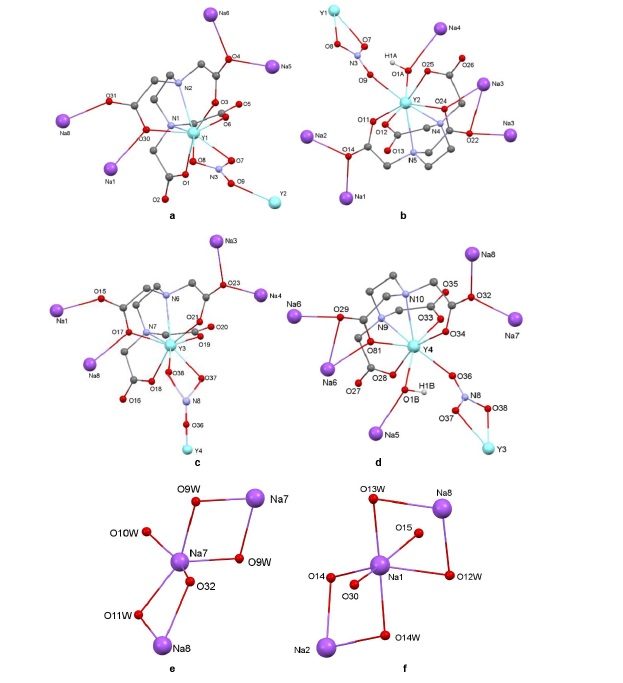
 Abstract: Heterometallic f/s-block complexes are not plentiful but play pivotal roles in understanding metal synergy in materials science and catalysis. Reaction of Y(NO3)3.6H2O with EDTANa2.2H2O (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, disodium salt dihydrate) gives the dodecanuclear {Y4Na8(L)4(OH)2(NO3)2(H2O)16} (1). Complex (1) is characterized by elemental analyses, IR and conductance measurement. The structure of (1) was elucidated by X-ray diffraction analysis. The compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with the following parameters: a = 24.81289 (15) Å, b = 15.63590 (8) Å, c = 19.68764 (14) Å, ??= 106.6623 (7)°, V = 7317.53 (8) Å3, Z= 4, R1 = 0.041, wR2 = 0.117. The asymmetric unit of the compound contains four tetradeprotonated (L4-) EDTA molecules, four octacoordinated yttrium ions, three pentacoordinated sodium ions, five hexacoordinated sodium ions, two chelating nitrate groups, two hydroxy groups acting in u2-mode, seven coordinated water molecules acting in n1-mode and nine coordinated water molecules acting in n2-mode. Each of the YIII cations is coordinated by one fully deprotonated EDTA which link also four NaI cations. Each of the NO3- anions bridge two YIII ions, while each of the two hydroxy groups bride one YIII cation and one NaI cation. The environment around the octacoordinated YIII cations are best described as a square antiprisms. The environments around the pentacoordinated NaI ions are best described as a square pyramidal geometries, while the hexacoordinated NaI ions exhibit octahedral environments. The molecule features a typical 3D hydrogen-bonded network with diverse coordination geometries (square antiprismatic Y³?, square pyramidal/octahedral Na?). Abstract: Heterometallic f/s-block complexes are not plentiful but play pivotal roles in understanding metal synergy in materials science and catalysis. Reaction of Y(NO3)3.6H2O with EDTANa2.2H2O (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, disodium salt dihydrate) gives the dodecanuclear {Y4Na8(L)4(OH)2(NO3)2(H2O)16} (1). Complex (1) is characterized by elemental analyses, IR and conductance measurement. The structure of (1) was elucidated by X-ray diffraction analysis. The compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with the following parameters: a = 24.81289 (15) Å, b = 15.63590 (8) Å, c = 19.68764 (14) Å, ??= 106.6623 (7)°, V = 7317.53 (8) Å3, Z= 4, R1 = 0.041, wR2 = 0.117. The asymmetric unit of the compound contains four tetradeprotonated (L4-) EDTA molecules, four octacoordinated yttrium ions, three pentacoordinated sodium ions, five hexacoordinated sodium ions, two chelating nitrate groups, two hydroxy groups acting in u2-mode, seven coordinated water molecules acting in n1-mode and nine coordinated water molecules acting in n2-mode. Each of the YIII cations is coordinated by one fully deprotonated EDTA which link also four NaI cations. Each of the NO3- anions bridge two YIII ions, while each of the two hydroxy groups bride one YIII cation and one NaI cation. The environment around the octacoordinated YIII cations are best described as a square antiprisms. The environments around the pentacoordinated NaI ions are best described as a square pyramidal geometries, while the hexacoordinated NaI ions exhibit octahedral environments. The molecule features a typical 3D hydrogen-bonded network with diverse coordination geometries (square antiprismatic Y³?, square pyramidal/octahedral Na?). |





 Abstract: Heterometallic f/s-block complexes are not plentiful but play pivotal roles in understanding metal synergy in materials science and catalysis. Reaction of Y(NO3)3.6H2O with EDTANa2.2H2O (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, disodium salt dihydrate) gives the dodecanuclear {Y4Na8(L)4(OH)2(NO3)2(H2O)16} (1). Complex (1) is characterized by elemental analyses, IR and conductance measurement. The structure of (1) was elucidated by X-ray diffraction analysis. The compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with the following parameters: a = 24.81289 (15) Å, b = 15.63590 (8) Å, c = 19.68764 (14) Å, ??= 106.6623 (7)°, V = 7317.53 (8) Å3, Z= 4, R1 = 0.041, wR2 = 0.117. The asymmetric unit of the compound contains four tetradeprotonated (L4-) EDTA molecules, four octacoordinated yttrium ions, three pentacoordinated sodium ions, five hexacoordinated sodium ions, two chelating nitrate groups, two hydroxy groups acting in u2-mode, seven coordinated water molecules acting in n1-mode and nine coordinated water molecules acting in n2-mode. Each of the YIII cations is coordinated by one fully deprotonated EDTA which link also four NaI cations. Each of the NO3- anions bridge two YIII ions, while each of the two hydroxy groups bride one YIII cation and one NaI cation. The environment around the octacoordinated YIII cations are best described as a square antiprisms. The environments around the pentacoordinated NaI ions are best described as a square pyramidal geometries, while the hexacoordinated NaI ions exhibit octahedral environments. The molecule features a typical 3D hydrogen-bonded network with diverse coordination geometries (square antiprismatic Y³?, square pyramidal/octahedral Na?).
Abstract: Heterometallic f/s-block complexes are not plentiful but play pivotal roles in understanding metal synergy in materials science and catalysis. Reaction of Y(NO3)3.6H2O with EDTANa2.2H2O (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, disodium salt dihydrate) gives the dodecanuclear {Y4Na8(L)4(OH)2(NO3)2(H2O)16} (1). Complex (1) is characterized by elemental analyses, IR and conductance measurement. The structure of (1) was elucidated by X-ray diffraction analysis. The compound crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with the following parameters: a = 24.81289 (15) Å, b = 15.63590 (8) Å, c = 19.68764 (14) Å, ??= 106.6623 (7)°, V = 7317.53 (8) Å3, Z= 4, R1 = 0.041, wR2 = 0.117. The asymmetric unit of the compound contains four tetradeprotonated (L4-) EDTA molecules, four octacoordinated yttrium ions, three pentacoordinated sodium ions, five hexacoordinated sodium ions, two chelating nitrate groups, two hydroxy groups acting in u2-mode, seven coordinated water molecules acting in n1-mode and nine coordinated water molecules acting in n2-mode. Each of the YIII cations is coordinated by one fully deprotonated EDTA which link also four NaI cations. Each of the NO3- anions bridge two YIII ions, while each of the two hydroxy groups bride one YIII cation and one NaI cation. The environment around the octacoordinated YIII cations are best described as a square antiprisms. The environments around the pentacoordinated NaI ions are best described as a square pyramidal geometries, while the hexacoordinated NaI ions exhibit octahedral environments. The molecule features a typical 3D hydrogen-bonded network with diverse coordination geometries (square antiprismatic Y³?, square pyramidal/octahedral Na?). @article={003244613,author = {FALL, Ndiouga; DIOP, Amar; SECK, Thierno Moussa; THIAM, Ibrahima Elhadji; DIOUF, Ousmane; ELLENA, Javier; GAYE, Mohamed.},title={Synthesis and structural elucidation of a novel hetero-dodecametallic yttrium-sodium complex based on EDTA: insights into f/s-block coordination chemistry},journal={International Research Journal of Pure and Applied Chemistry},note={v. 26, n. 3, p. 13400-11-13400-23},year={2025}}
@article={003244613,author = {FALL, Ndiouga; DIOP, Amar; SECK, Thierno Moussa; THIAM, Ibrahima Elhadji; DIOUF, Ousmane; ELLENA, Javier; GAYE, Mohamed.},title={Synthesis and structural elucidation of a novel hetero-dodecametallic yttrium-sodium complex based on EDTA: insights into f/s-block coordination chemistry},journal={International Research Journal of Pure and Applied Chemistry},note={v. 26, n. 3, p. 13400-11-13400-23},year={2025}}