Carbon doping in small lithium clusters: structural, energetic, and electronic properties from quantum Monte Carlo calculations.
BRITO, Braulio Gabriel Alencar; HAI, Guo-Qiang; CÂNDIDO, Ladir.
BRITO, Braulio Gabriel Alencar; HAI, Guo-Qiang; CÂNDIDO, Ladir.





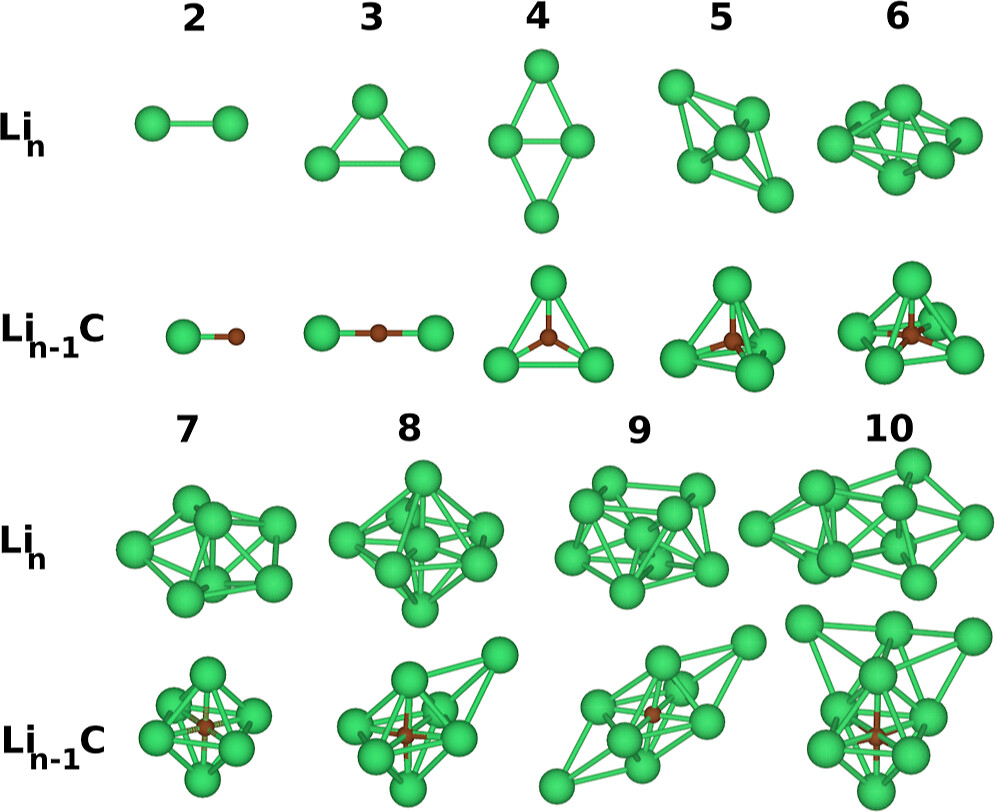 Abstract: We investigate the energetic and structural properties of small lithium clusters doped with a carbon atom using a combination of computational methods, including density functional theory (DFT), diffusion quantum Monte Carlo (DMC), and the Hartree-Fock (HF) approximation. We calculate the lowest energy structures, total ground-state energies, electron populations, binding energies, and dissociation energies as a function of cluster size. Our results show that carbon doping significantly enhances the stability of lithium clusters, increasing the magnitude of the binding energy by 0.261 ± 0.008 to 1.048 ± 0.003 eV. Carbon substitution also reduces the bond length by approximately 1.00 Å and decreases the coordination number by up to 2.78. The dissociation energy required to remove the doped carbon atom ranges from -7.65 ± 0.02 to -3.33 ± 0.01 eV, which is substantially larger in magnitude than the energy required to remove a lithium atom, varying from -2.81 ± 0.02 to -0.78 ± 0.02 eV. These results indicate that carbon doping enhances cluster stability, as reflected by the increased dissociation energy and changes in bonding characteristics. We compare our findings with available theoretical and experimental data, providing valuable insights into the role of carbon doping in strengthening the stability and bonding properties of lithium clusters.
Abstract: We investigate the energetic and structural properties of small lithium clusters doped with a carbon atom using a combination of computational methods, including density functional theory (DFT), diffusion quantum Monte Carlo (DMC), and the Hartree-Fock (HF) approximation. We calculate the lowest energy structures, total ground-state energies, electron populations, binding energies, and dissociation energies as a function of cluster size. Our results show that carbon doping significantly enhances the stability of lithium clusters, increasing the magnitude of the binding energy by 0.261 ± 0.008 to 1.048 ± 0.003 eV. Carbon substitution also reduces the bond length by approximately 1.00 Å and decreases the coordination number by up to 2.78. The dissociation energy required to remove the doped carbon atom ranges from -7.65 ± 0.02 to -3.33 ± 0.01 eV, which is substantially larger in magnitude than the energy required to remove a lithium atom, varying from -2.81 ± 0.02 to -0.78 ± 0.02 eV. These results indicate that carbon doping enhances cluster stability, as reflected by the increased dissociation energy and changes in bonding characteristics. We compare our findings with available theoretical and experimental data, providing valuable insights into the role of carbon doping in strengthening the stability and bonding properties of lithium clusters. @article={003234028,author = {BRITO, Braulio Gabriel Alencar; HAI, Guo-Qiang; CÂNDIDO, Ladir.},title={Carbon doping in small lithium clusters: structural, energetic, and electronic properties from quantum Monte Carlo calculations},journal={ACS Omega},note={v. 10, n. 2, p. 2296-2304},year={2025}}
@article={003234028,author = {BRITO, Braulio Gabriel Alencar; HAI, Guo-Qiang; CÂNDIDO, Ladir.},title={Carbon doping in small lithium clusters: structural, energetic, and electronic properties from quantum Monte Carlo calculations},journal={ACS Omega},note={v. 10, n. 2, p. 2296-2304},year={2025}}