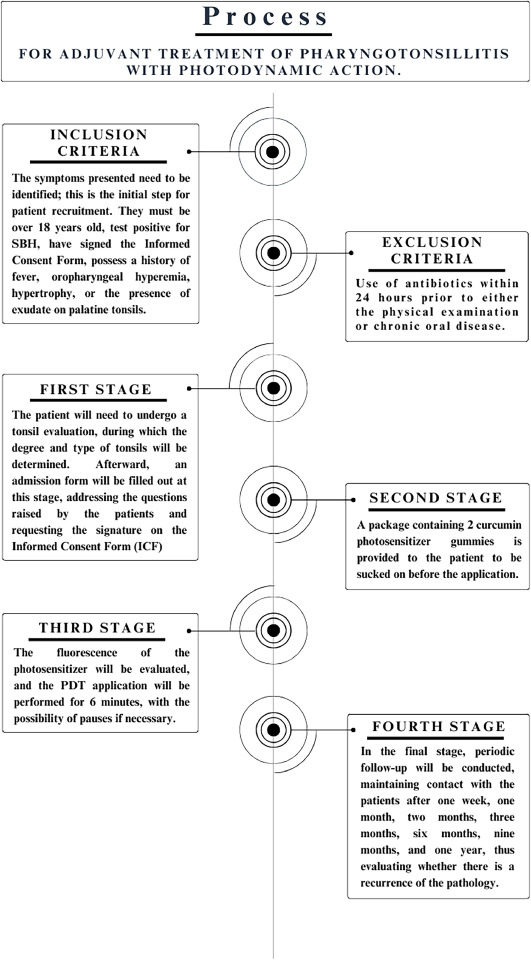
 Abstract: Background: Pharyngotonsillitis (PT) is an inflammatory and infectious condition affecting the tonsils in the oropharynx, predominantly caused by a variety of viral, fungal, and bacterial pathogens, including Streptococcus pyogenes. With the increasing challenge of antibiotic resistance, alternative therapeutic approaches are needed. Methods: This study explores the effectiveness and safety of Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) as a therapeutic approach for managing acute PT. PDT involves the use of a photosensitizer, light, and molecular oxygen. We utilized a curcumin-based photosensitizer incorporated into a gum formulation, followed by exposure to blue LED irradiation (455 ± 30 nm, intensity of 200 mW for 6 min) with 1 to 2 PDT sessions depending on the clinical case. Results: The treatment's impact was assessed through systematic monitoring of clinical progression post-treatment, encompassing clinical history, examination, and follow-up. In all three cases examined, PDT was observed to effectively eradicate the infection and prevent its recurrence during the period evaluated. Conclusion: Photodynamic Therapy, using a curcumin-based photosensitizer and blue LED light, appears to be a promising alternative to traditional antibiotics for the treatment of PT, demonstrating both efficacy in infection eradication and safety in application. Further studies are recommended to substantiate these findings and explore long-term outcomes. Abstract: Background: Pharyngotonsillitis (PT) is an inflammatory and infectious condition affecting the tonsils in the oropharynx, predominantly caused by a variety of viral, fungal, and bacterial pathogens, including Streptococcus pyogenes. With the increasing challenge of antibiotic resistance, alternative therapeutic approaches are needed. Methods: This study explores the effectiveness and safety of Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) as a therapeutic approach for managing acute PT. PDT involves the use of a photosensitizer, light, and molecular oxygen. We utilized a curcumin-based photosensitizer incorporated into a gum formulation, followed by exposure to blue LED irradiation (455 ± 30 nm, intensity of 200 mW for 6 min) with 1 to 2 PDT sessions depending on the clinical case. Results: The treatment's impact was assessed through systematic monitoring of clinical progression post-treatment, encompassing clinical history, examination, and follow-up. In all three cases examined, PDT was observed to effectively eradicate the infection and prevent its recurrence during the period evaluated. Conclusion: Photodynamic Therapy, using a curcumin-based photosensitizer and blue LED light, appears to be a promising alternative to traditional antibiotics for the treatment of PT, demonstrating both efficacy in infection eradication and safety in application. Further studies are recommended to substantiate these findings and explore long-term outcomes. |





 Abstract: Background: Pharyngotonsillitis (PT) is an inflammatory and infectious condition affecting the tonsils in the oropharynx, predominantly caused by a variety of viral, fungal, and bacterial pathogens, including Streptococcus pyogenes. With the increasing challenge of antibiotic resistance, alternative therapeutic approaches are needed. Methods: This study explores the effectiveness and safety of Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) as a therapeutic approach for managing acute PT. PDT involves the use of a photosensitizer, light, and molecular oxygen. We utilized a curcumin-based photosensitizer incorporated into a gum formulation, followed by exposure to blue LED irradiation (455 ± 30 nm, intensity of 200 mW for 6 min) with 1 to 2 PDT sessions depending on the clinical case. Results: The treatment's impact was assessed through systematic monitoring of clinical progression post-treatment, encompassing clinical history, examination, and follow-up. In all three cases examined, PDT was observed to effectively eradicate the infection and prevent its recurrence during the period evaluated. Conclusion: Photodynamic Therapy, using a curcumin-based photosensitizer and blue LED light, appears to be a promising alternative to traditional antibiotics for the treatment of PT, demonstrating both efficacy in infection eradication and safety in application. Further studies are recommended to substantiate these findings and explore long-term outcomes.
Abstract: Background: Pharyngotonsillitis (PT) is an inflammatory and infectious condition affecting the tonsils in the oropharynx, predominantly caused by a variety of viral, fungal, and bacterial pathogens, including Streptococcus pyogenes. With the increasing challenge of antibiotic resistance, alternative therapeutic approaches are needed. Methods: This study explores the effectiveness and safety of Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) as a therapeutic approach for managing acute PT. PDT involves the use of a photosensitizer, light, and molecular oxygen. We utilized a curcumin-based photosensitizer incorporated into a gum formulation, followed by exposure to blue LED irradiation (455 ± 30 nm, intensity of 200 mW for 6 min) with 1 to 2 PDT sessions depending on the clinical case. Results: The treatment's impact was assessed through systematic monitoring of clinical progression post-treatment, encompassing clinical history, examination, and follow-up. In all three cases examined, PDT was observed to effectively eradicate the infection and prevent its recurrence during the period evaluated. Conclusion: Photodynamic Therapy, using a curcumin-based photosensitizer and blue LED light, appears to be a promising alternative to traditional antibiotics for the treatment of PT, demonstrating both efficacy in infection eradication and safety in application. Further studies are recommended to substantiate these findings and explore long-term outcomes. @article={003215517,author = {DUARTE, Laíza Mohana Pinheiro; SANTIAGO, Isabella Dotta Damha; BLANCO, Kate Cristina; BAGNATO, Vanderlei Salvador.},title={Use of photodynamic therapy to combat recurrent pharyngotonsillitis: three case reports},journal={Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy},note={v. 49, p. 104312-1-104312-7},year={2024}}
@article={003215517,author = {DUARTE, Laíza Mohana Pinheiro; SANTIAGO, Isabella Dotta Damha; BLANCO, Kate Cristina; BAGNATO, Vanderlei Salvador.},title={Use of photodynamic therapy to combat recurrent pharyngotonsillitis: three case reports},journal={Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy},note={v. 49, p. 104312-1-104312-7},year={2024}}