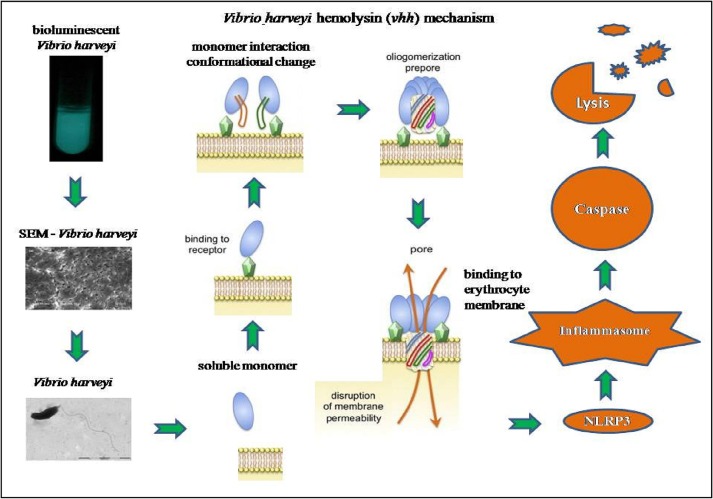
 Abstract: Shrimp culture systems are being affected by bacterial diseases particularly Vibrios. Use of therapeutic agents in shrimp culture has lead to the resistance among aquatic bacteria. Accordingly, health management becomes of major importance in aquaculture. Under this situation, developing bio-inhibitors from natural marine resources which are most appropriate, which is considered as an unmatched reservoir of several biological products. Molecular docking is suited to a major approach in structural biology and computer-assisted drug design against the proteins of disease-causative agents. In the present study, marine macroalga Kappaphycus alvarezii was used for developing inhibitors against bioluminescence disease-causing pathogenic bacteria Vibrio harveyi. K. alvarezii was collected from the Mandapam, Tamil Nadu, India. Ethyl acetate based extract of K. alvarezii was tested against the growth and virulence factors of V. harveyi during Penaeus monodon larviculture. Further K. alvarezii extract was subjected to GC-MS analysis to identify the biomolecules. The homology modelling of the virulent protein, hemolysin of V. harveyi was designed during this study. Hence, it was aimed at molecular docking against the biomolecules identified from K. alvarezii extract. During shrimp larviculture, the extract of K. alvarezii (200 µg mL-1) exhibited a reduction on Cumulative Percentage of Mortality (29.70 %) in postlarvae against the challenge of V. harveyi infection. Among the compounds docked, an inhibitory effect was observed based on docking scores and were found the highest binding affinity/inhibiting activity in Cyclotetracosane with the least energy required with a docking score of binding energy -7.66 kcal/mol, inhibition constant 0.002 mM and intermolecular efficiency -0.32 kcal/mol. Using statistical analysis, significant differences (p < 0.05) were observed between the growth and virulence factors of V. harveyi during shrimp larviculture trials. While considering these findings, it was determined that K. alvarezii extract can be replaced as an alternative bio-agents protecting against infections caused by V. harveyi and possibly other aquatic pathogenic bacteria in shrimp farming systems. Abstract: Shrimp culture systems are being affected by bacterial diseases particularly Vibrios. Use of therapeutic agents in shrimp culture has lead to the resistance among aquatic bacteria. Accordingly, health management becomes of major importance in aquaculture. Under this situation, developing bio-inhibitors from natural marine resources which are most appropriate, which is considered as an unmatched reservoir of several biological products. Molecular docking is suited to a major approach in structural biology and computer-assisted drug design against the proteins of disease-causative agents. In the present study, marine macroalga Kappaphycus alvarezii was used for developing inhibitors against bioluminescence disease-causing pathogenic bacteria Vibrio harveyi. K. alvarezii was collected from the Mandapam, Tamil Nadu, India. Ethyl acetate based extract of K. alvarezii was tested against the growth and virulence factors of V. harveyi during Penaeus monodon larviculture. Further K. alvarezii extract was subjected to GC-MS analysis to identify the biomolecules. The homology modelling of the virulent protein, hemolysin of V. harveyi was designed during this study. Hence, it was aimed at molecular docking against the biomolecules identified from K. alvarezii extract. During shrimp larviculture, the extract of K. alvarezii (200 µg mL-1) exhibited a reduction on Cumulative Percentage of Mortality (29.70 %) in postlarvae against the challenge of V. harveyi infection. Among the compounds docked, an inhibitory effect was observed based on docking scores and were found the highest binding affinity/inhibiting activity in Cyclotetracosane with the least energy required with a docking score of binding energy -7.66 kcal/mol, inhibition constant 0.002 mM and intermolecular efficiency -0.32 kcal/mol. Using statistical analysis, significant differences (p < 0.05) were observed between the growth and virulence factors of V. harveyi during shrimp larviculture trials. While considering these findings, it was determined that K. alvarezii extract can be replaced as an alternative bio-agents protecting against infections caused by V. harveyi and possibly other aquatic pathogenic bacteria in shrimp farming systems. |





 Abstract: Shrimp culture systems are being affected by bacterial diseases particularly Vibrios. Use of therapeutic agents in shrimp culture has lead to the resistance among aquatic bacteria. Accordingly, health management becomes of major importance in aquaculture. Under this situation, developing bio-inhibitors from natural marine resources which are most appropriate, which is considered as an unmatched reservoir of several biological products. Molecular docking is suited to a major approach in structural biology and computer-assisted drug design against the proteins of disease-causative agents. In the present study, marine macroalga Kappaphycus alvarezii was used for developing inhibitors against bioluminescence disease-causing pathogenic bacteria Vibrio harveyi. K. alvarezii was collected from the Mandapam, Tamil Nadu, India. Ethyl acetate based extract of K. alvarezii was tested against the growth and virulence factors of V. harveyi during Penaeus monodon larviculture. Further K. alvarezii extract was subjected to GC-MS analysis to identify the biomolecules. The homology modelling of the virulent protein, hemolysin of V. harveyi was designed during this study. Hence, it was aimed at molecular docking against the biomolecules identified from K. alvarezii extract. During shrimp larviculture, the extract of K. alvarezii (200 µg mL-1) exhibited a reduction on Cumulative Percentage of Mortality (29.70 %) in postlarvae against the challenge of V. harveyi infection. Among the compounds docked, an inhibitory effect was observed based on docking scores and were found the highest binding affinity/inhibiting activity in Cyclotetracosane with the least energy required with a docking score of binding energy -7.66 kcal/mol, inhibition constant 0.002 mM and intermolecular efficiency -0.32 kcal/mol. Using statistical analysis, significant differences (p < 0.05) were observed between the growth and virulence factors of V. harveyi during shrimp larviculture trials. While considering these findings, it was determined that K. alvarezii extract can be replaced as an alternative bio-agents protecting against infections caused by V. harveyi and possibly other aquatic pathogenic bacteria in shrimp farming systems.
Abstract: Shrimp culture systems are being affected by bacterial diseases particularly Vibrios. Use of therapeutic agents in shrimp culture has lead to the resistance among aquatic bacteria. Accordingly, health management becomes of major importance in aquaculture. Under this situation, developing bio-inhibitors from natural marine resources which are most appropriate, which is considered as an unmatched reservoir of several biological products. Molecular docking is suited to a major approach in structural biology and computer-assisted drug design against the proteins of disease-causative agents. In the present study, marine macroalga Kappaphycus alvarezii was used for developing inhibitors against bioluminescence disease-causing pathogenic bacteria Vibrio harveyi. K. alvarezii was collected from the Mandapam, Tamil Nadu, India. Ethyl acetate based extract of K. alvarezii was tested against the growth and virulence factors of V. harveyi during Penaeus monodon larviculture. Further K. alvarezii extract was subjected to GC-MS analysis to identify the biomolecules. The homology modelling of the virulent protein, hemolysin of V. harveyi was designed during this study. Hence, it was aimed at molecular docking against the biomolecules identified from K. alvarezii extract. During shrimp larviculture, the extract of K. alvarezii (200 µg mL-1) exhibited a reduction on Cumulative Percentage of Mortality (29.70 %) in postlarvae against the challenge of V. harveyi infection. Among the compounds docked, an inhibitory effect was observed based on docking scores and were found the highest binding affinity/inhibiting activity in Cyclotetracosane with the least energy required with a docking score of binding energy -7.66 kcal/mol, inhibition constant 0.002 mM and intermolecular efficiency -0.32 kcal/mol. Using statistical analysis, significant differences (p < 0.05) were observed between the growth and virulence factors of V. harveyi during shrimp larviculture trials. While considering these findings, it was determined that K. alvarezii extract can be replaced as an alternative bio-agents protecting against infections caused by V. harveyi and possibly other aquatic pathogenic bacteria in shrimp farming systems. @article={003147491,author = {SIVAKUMAR, Krishnamoorthy; KANNAPPAN, Sudalayandi; BALAKRISHNAN, Vijayakumar.},title={Molecular docking approaches of biomolecules extracted from red seaweed Kappaphycus alvarezii against hemolysin protein of bioluminescence disease-causing bacteria Vibrio harveyi},journal={Algal Research},note={v. 74, p. 103207-1-103207-16 + supplementary data},year={2023}}
@article={003147491,author = {SIVAKUMAR, Krishnamoorthy; KANNAPPAN, Sudalayandi; BALAKRISHNAN, Vijayakumar.},title={Molecular docking approaches of biomolecules extracted from red seaweed Kappaphycus alvarezii against hemolysin protein of bioluminescence disease-causing bacteria Vibrio harveyi},journal={Algal Research},note={v. 74, p. 103207-1-103207-16 + supplementary data},year={2023}}