Electrocatalytic oxidation of ethinyl estradiol by an iron oxide nanoparticle/nickel phthalocyanine supramolecular electrode.
RIBEIRO, Camila L.; SOUZA, Jurandir Rodrigues de; SILVA, Marcelo de Assumpção Pereira da; SANTOS JUNIOR, Vianney O.; PATERNO, Leonardo G.
RIBEIRO, Camila L.; SOUZA, Jurandir Rodrigues de; SILVA, Marcelo de Assumpção Pereira da; SANTOS JUNIOR, Vianney O.; PATERNO, Leonardo G.





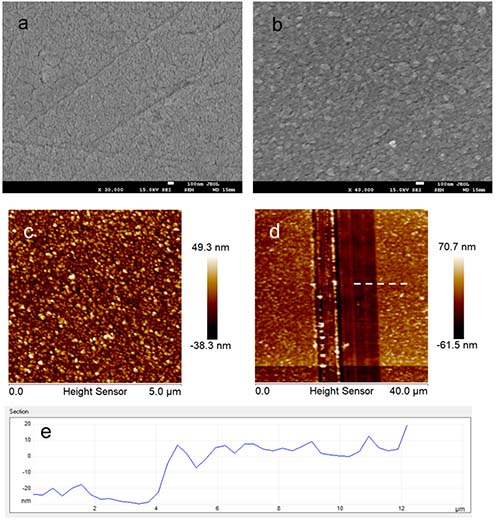 Abstract: Indium-doped tin oxide (ITO) substrates were surface-modified with layer-by-layer nanocomposite films of anionic nickel(II) tetrasulfonated phthalocyanine (NiTsPc) and positively charged iron oxide nanoparticles (IONs) aiming at the electrocatalytic oxidation of ethinyl estradiol (EE2). Atomic force microscopy and UV?vis and Raman spectroscopies suggest that the successive deposition of NiTsPc/ION bilayers forms a porous supramolecular structure driven by both electrostatic interaction and covalent Fe(III)-O-Ni(II) bridges. Cyclic and differential pulse voltammetry show that EE2 is effectively oxidized at the ITO/(NiTsPc/ION) electrode while displaying an isolated and well-defined peak at +0.73 V (vs Ag/AgCl). Conversely, bare ITO and ITO modified by either ION or NiTsPc alone are unable to oxidize EE2. The benefit of the NiTsPc/ION bilayers for the EE2 oxidation is assigned to the charge-transfer process occurring between IONs and NiTsPc through the Fe(III)-O-Ni(II) bridge. This process suppresses the oxidation of both the phthalocyanine ring and Ni(II), which appear in the same potential range of EE2 oxidation and allow the electrons to be transferred from EE2 adsorbed onto IONs to the ITO substrate underneath. Therefore, this new sensing platform operates under a particular working principle in which analyte oxidation and subsequent charge transport are separately performed by its individual components.
Abstract: Indium-doped tin oxide (ITO) substrates were surface-modified with layer-by-layer nanocomposite films of anionic nickel(II) tetrasulfonated phthalocyanine (NiTsPc) and positively charged iron oxide nanoparticles (IONs) aiming at the electrocatalytic oxidation of ethinyl estradiol (EE2). Atomic force microscopy and UV?vis and Raman spectroscopies suggest that the successive deposition of NiTsPc/ION bilayers forms a porous supramolecular structure driven by both electrostatic interaction and covalent Fe(III)-O-Ni(II) bridges. Cyclic and differential pulse voltammetry show that EE2 is effectively oxidized at the ITO/(NiTsPc/ION) electrode while displaying an isolated and well-defined peak at +0.73 V (vs Ag/AgCl). Conversely, bare ITO and ITO modified by either ION or NiTsPc alone are unable to oxidize EE2. The benefit of the NiTsPc/ION bilayers for the EE2 oxidation is assigned to the charge-transfer process occurring between IONs and NiTsPc through the Fe(III)-O-Ni(II) bridge. This process suppresses the oxidation of both the phthalocyanine ring and Ni(II), which appear in the same potential range of EE2 oxidation and allow the electrons to be transferred from EE2 adsorbed onto IONs to the ITO substrate underneath. Therefore, this new sensing platform operates under a particular working principle in which analyte oxidation and subsequent charge transport are separately performed by its individual components. @article={003004747,author = {RIBEIRO, Camila L.; SOUZA, Jurandir Rodrigues de; SILVA, Marcelo de Assumpção Pereira da; SANTOS JUNIOR, Vianney O.; PATERNO, Leonardo G.},title={Electrocatalytic oxidation of ethinyl estradiol by an iron oxide nanoparticle/nickel phthalocyanine supramolecular electrode},journal={Journal of Physical Chemistry C},note={v. 124, n. 35, p. 19057-19069 + supporting information},year={2020}}
@article={003004747,author = {RIBEIRO, Camila L.; SOUZA, Jurandir Rodrigues de; SILVA, Marcelo de Assumpção Pereira da; SANTOS JUNIOR, Vianney O.; PATERNO, Leonardo G.},title={Electrocatalytic oxidation of ethinyl estradiol by an iron oxide nanoparticle/nickel phthalocyanine supramolecular electrode},journal={Journal of Physical Chemistry C},note={v. 124, n. 35, p. 19057-19069 + supporting information},year={2020}}