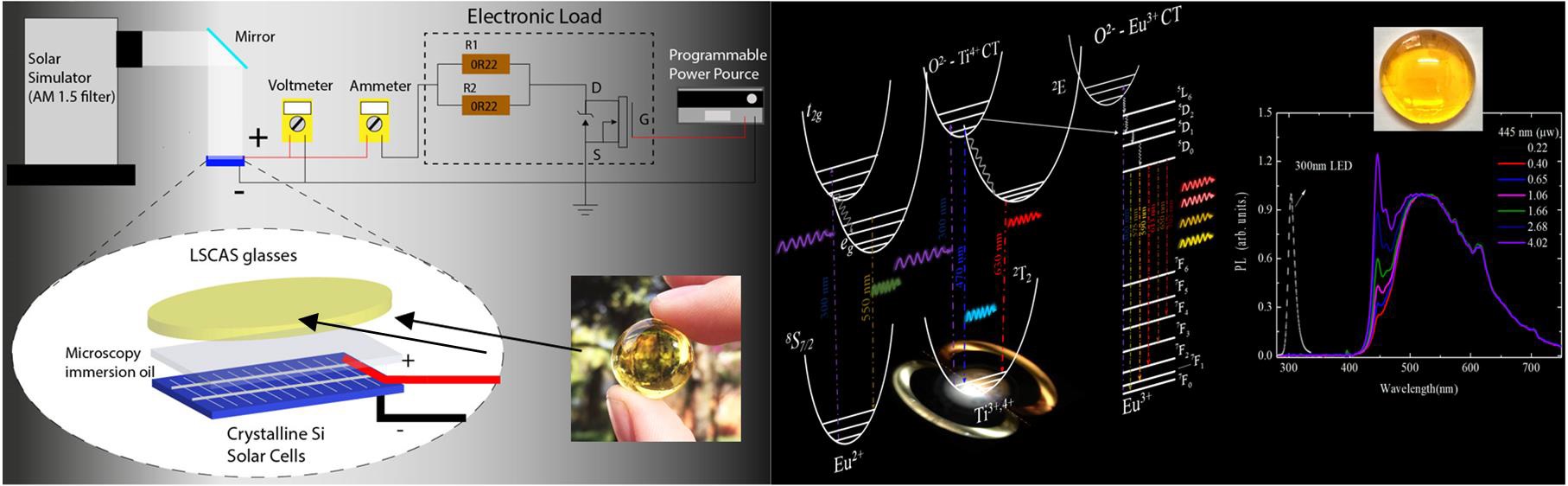
 Abstract: In the last decades many efforts have been done in order to obtain new materials for the development of more efficient solar cells and tunable white lighting. OH- free low silica calcium aluminosilicate glasses (LSCAS) have been attracting attention towards these applications owing to their high resistance against chemical degradation, high transparency from the UV to the near infrared (~5 µm) spectral regions, excellent optical quality, superior thermomechanical properties and low phonon energies (~850 cm 1) compared to other oxide glasses [1-5]. When doped with Ce, Ce-Eu, Eu-Pr and Eu-Ti these glasses presented broad emission bands towards the visible range, suggesting this system as a promising candidate for tunable artificial lighting [1-4]. On the other hand, solar panels efficiency is known to be highly dependent on the spectral matching between the solar spectrum and the active material band-gap. Much effort has been done towards the development of new solar energy absorbers aiming efficient downconversion processes to convert high energy photons from the visible range into low-energy ones close to the silicon band gap in the near infrared, being therefore sensitizers to improve the performance of the silicon solar cells [5]. In this live, an up to date review on the luminescence properties of ion doped LSCAS glasses will be discussed. C omparison between other family of optical glasses and crystalline phosphors will be made. The glasses were melted under vacuum atmosphere to minimize OH- molecules absorption in the near infrared region, improving therefore their luminescence quantum yield. In addition, this melting procedure has been shown to facilitate the tailoring of different oxidation states of the doping ions in the glass structure, allowing to play with the energy transfer process to enhance specific emissions. The focus will be on possible applications as spectral converters for efficient emission at the silicon band gap for solar cells, with special attention to the glasses co-doped with Eu, Nd and Yb ions, and also as glasses for tunable white lighting when doped with Ce, Eu, Pr and Ti ions, emphasizing possible advantages in eventual future applications as noncrystalline WLEDs devices. Abstract: In the last decades many efforts have been done in order to obtain new materials for the development of more efficient solar cells and tunable white lighting. OH- free low silica calcium aluminosilicate glasses (LSCAS) have been attracting attention towards these applications owing to their high resistance against chemical degradation, high transparency from the UV to the near infrared (~5 µm) spectral regions, excellent optical quality, superior thermomechanical properties and low phonon energies (~850 cm 1) compared to other oxide glasses [1-5]. When doped with Ce, Ce-Eu, Eu-Pr and Eu-Ti these glasses presented broad emission bands towards the visible range, suggesting this system as a promising candidate for tunable artificial lighting [1-4]. On the other hand, solar panels efficiency is known to be highly dependent on the spectral matching between the solar spectrum and the active material band-gap. Much effort has been done towards the development of new solar energy absorbers aiming efficient downconversion processes to convert high energy photons from the visible range into low-energy ones close to the silicon band gap in the near infrared, being therefore sensitizers to improve the performance of the silicon solar cells [5]. In this live, an up to date review on the luminescence properties of ion doped LSCAS glasses will be discussed. C omparison between other family of optical glasses and crystalline phosphors will be made. The glasses were melted under vacuum atmosphere to minimize OH- molecules absorption in the near infrared region, improving therefore their luminescence quantum yield. In addition, this melting procedure has been shown to facilitate the tailoring of different oxidation states of the doping ions in the glass structure, allowing to play with the energy transfer process to enhance specific emissions. The focus will be on possible applications as spectral converters for efficient emission at the silicon band gap for solar cells, with special attention to the glasses co-doped with Eu, Nd and Yb ions, and also as glasses for tunable white lighting when doped with Ce, Eu, Pr and Ti ions, emphasizing possible advantages in eventual future applications as noncrystalline WLEDs devices. |




 Abstract: In the last decades many efforts have been done in order to obtain new materials for the development of more efficient solar cells and tunable white lighting. OH- free low silica calcium aluminosilicate glasses (LSCAS) have been attracting attention towards these applications owing to their high resistance against chemical degradation, high transparency from the UV to the near infrared (~5 µm) spectral regions, excellent optical quality, superior thermomechanical properties and low phonon energies (~850 cm 1) compared to other oxide glasses [1-5]. When doped with Ce, Ce-Eu, Eu-Pr and Eu-Ti these glasses presented broad emission bands towards the visible range, suggesting this system as a promising candidate for tunable artificial lighting [1-4]. On the other hand, solar panels efficiency is known to be highly dependent on the spectral matching between the solar spectrum and the active material band-gap. Much effort has been done towards the development of new solar energy absorbers aiming efficient downconversion processes to convert high energy photons from the visible range into low-energy ones close to the silicon band gap in the near infrared, being therefore sensitizers to improve the performance of the silicon solar cells [5]. In this live, an up to date review on the luminescence properties of ion doped LSCAS glasses will be discussed. C omparison between other family of optical glasses and crystalline phosphors will be made. The glasses were melted under vacuum atmosphere to minimize OH- molecules absorption in the near infrared region, improving therefore their luminescence quantum yield. In addition, this melting procedure has been shown to facilitate the tailoring of different oxidation states of the doping ions in the glass structure, allowing to play with the energy transfer process to enhance specific emissions. The focus will be on possible applications as spectral converters for efficient emission at the silicon band gap for solar cells, with special attention to the glasses co-doped with Eu, Nd and Yb ions, and also as glasses for tunable white lighting when doped with Ce, Eu, Pr and Ti ions, emphasizing possible advantages in eventual future applications as noncrystalline WLEDs devices.
Abstract: In the last decades many efforts have been done in order to obtain new materials for the development of more efficient solar cells and tunable white lighting. OH- free low silica calcium aluminosilicate glasses (LSCAS) have been attracting attention towards these applications owing to their high resistance against chemical degradation, high transparency from the UV to the near infrared (~5 µm) spectral regions, excellent optical quality, superior thermomechanical properties and low phonon energies (~850 cm 1) compared to other oxide glasses [1-5]. When doped with Ce, Ce-Eu, Eu-Pr and Eu-Ti these glasses presented broad emission bands towards the visible range, suggesting this system as a promising candidate for tunable artificial lighting [1-4]. On the other hand, solar panels efficiency is known to be highly dependent on the spectral matching between the solar spectrum and the active material band-gap. Much effort has been done towards the development of new solar energy absorbers aiming efficient downconversion processes to convert high energy photons from the visible range into low-energy ones close to the silicon band gap in the near infrared, being therefore sensitizers to improve the performance of the silicon solar cells [5]. In this live, an up to date review on the luminescence properties of ion doped LSCAS glasses will be discussed. C omparison between other family of optical glasses and crystalline phosphors will be made. The glasses were melted under vacuum atmosphere to minimize OH- molecules absorption in the near infrared region, improving therefore their luminescence quantum yield. In addition, this melting procedure has been shown to facilitate the tailoring of different oxidation states of the doping ions in the glass structure, allowing to play with the energy transfer process to enhance specific emissions. The focus will be on possible applications as spectral converters for efficient emission at the silicon band gap for solar cells, with special attention to the glasses co-doped with Eu, Nd and Yb ions, and also as glasses for tunable white lighting when doped with Ce, Eu, Pr and Ti ions, emphasizing possible advantages in eventual future applications as noncrystalline WLEDs devices. @article={003025292,author = {BAESSO, M. L.; BENTO, A. C.; NOVATSKI, A.; ANDRADE, L. H. C.; LIMA, S. M.; NUNES, Luiz Antônio de Oliveira.},title={Optical glasses for smart white lighting and solar cells applications: where do we stand?},journal={Video Proceedings of Advanced Materials},note={v. 2, Article ID 2102107, Mar. 2021.},year={2021}}
@article={003025292,author = {BAESSO, M. L.; BENTO, A. C.; NOVATSKI, A.; ANDRADE, L. H. C.; LIMA, S. M.; NUNES, Luiz Antônio de Oliveira.},title={Optical glasses for smart white lighting and solar cells applications: where do we stand?},journal={Video Proceedings of Advanced Materials},note={v. 2, Article ID 2102107, Mar. 2021.},year={2021}}