Glutaminase affects the transcriptional activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ? (PPAR?) via direct interaction.
CASSAGO, Carolina Aparecida de Guzzi; DIAS, Marília Meira; PINHEIRO, Matheus Pinto; PASQUALI, Camila Cristina; BASTOS, Alliny Cristiny Silva; ISLAM, Zeyaul; CONSONNI, Sílvio Roberto; OLIVEIRA, Juliana Ferreira de; GOMES, Emerson Machi; ASCENÇÃO, Carolline Fernanda Rodrigues; HONORATO, Rodrigo; PAULETTI, Bianca Alves; INDOLFO, Nathalia de Carvalho; RIBEIRO FILHO, Helder Veras; OLIVEIRA, Paulo Sergio Lopes de; FIGUEIRA, Ana Carolina Migliorini; LEME, Adriana Franco Paes; AMBROSIO, André Luis Berteli; DIAS, Sandra Martha Gomes.
CASSAGO, Carolina Aparecida de Guzzi; DIAS, Marília Meira; PINHEIRO, Matheus Pinto; PASQUALI, Camila Cristina; BASTOS, Alliny Cristiny Silva; ISLAM, Zeyaul; CONSONNI, Sílvio Roberto; OLIVEIRA, Juliana Ferreira de; GOMES, Emerson Machi; ASCENÇÃO, Carolline Fernanda Rodrigues; HONORATO, Rodrigo; PAULETTI, Bianca Alves; INDOLFO, Nathalia de Carvalho; RIBEIRO FILHO, Helder Veras; OLIVEIRA, Paulo Sergio Lopes de; FIGUEIRA, Ana Carolina Migliorini; LEME, Adriana Franco Paes; AMBROSIO, André Luis Berteli; DIAS, Sandra Martha Gomes.
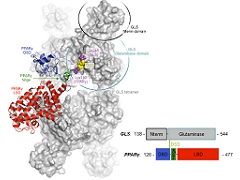 Abstract: Phosphate-activated glutaminases catalyze the deamidation of glutamine to glutamate and play key roles in several physiological and pathological processes. In humans, GLS encodes two multidomain splicing isoforms: KGA and GAC. In both isoforms, the canonical glutaminase domain is flanked by an N-terminal region that is folded into an EF-hand-like four-helix bundle. However, the splicing event replaces a well-structured three-repeat ankyrin domain in KGA with a shorter, unordered C-terminal stretch in GAC. The multidomain architecture, which contains putative protein-protein binding motifs, has led to speculation that glutaminases are involved in cellular processes other than glutamine metabolism; in fact, some proteins have been identified as binding partners of KGA and the isoforms of its paralogue gene, GLS2. Here, a yeast two-hybrid assay identified nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ? (PPAR?) as a new binding partner of the glutaminase. We show that KGA and GAC directly bind PPAR? with a low-micromolar dissociation constant; the interaction involves the N-terminal and catalytic domains of glutaminases as well as the ligand-binding domain of the nuclear receptor. The interaction occurs within the nucleus, and by sequestering PPAR? from its responsive element DR1, the glutaminases decreased nuclear receptor activity as assessed by a luciferase reporter assay. Altogether, our findings reveal an unexpected glutaminase-binding partner and, for the first time, directly link mitochondrial glutaminases to an unanticipated role in gene regulation. Abstract: Phosphate-activated glutaminases catalyze the deamidation of glutamine to glutamate and play key roles in several physiological and pathological processes. In humans, GLS encodes two multidomain splicing isoforms: KGA and GAC. In both isoforms, the canonical glutaminase domain is flanked by an N-terminal region that is folded into an EF-hand-like four-helix bundle. However, the splicing event replaces a well-structured three-repeat ankyrin domain in KGA with a shorter, unordered C-terminal stretch in GAC. The multidomain architecture, which contains putative protein-protein binding motifs, has led to speculation that glutaminases are involved in cellular processes other than glutamine metabolism; in fact, some proteins have been identified as binding partners of KGA and the isoforms of its paralogue gene, GLS2. Here, a yeast two-hybrid assay identified nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ? (PPAR?) as a new binding partner of the glutaminase. We show that KGA and GAC directly bind PPAR? with a low-micromolar dissociation constant; the interaction involves the N-terminal and catalytic domains of glutaminases as well as the ligand-binding domain of the nuclear receptor. The interaction occurs within the nucleus, and by sequestering PPAR? from its responsive element DR1, the glutaminases decreased nuclear receptor activity as assessed by a luciferase reporter assay. Altogether, our findings reveal an unexpected glutaminase-binding partner and, for the first time, directly link mitochondrial glutaminases to an unanticipated role in gene regulation. | |
| Biochemistry |
| v. 57, n. 44, p. 6293-6307 - Ano: 2018 |
| Fator de Impacto: 2,997 |
| http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00773 |  @article={002912043,author = {CASSAGO, Carolina Aparecida de Guzzi; DIAS, Marília Meira; PINHEIRO, Matheus Pinto; PASQUALI, Camila Cristina; BASTOS, Alliny Cristiny Silva; ISLAM, Zeyaul; CONSONNI, Sílvio Roberto; OLIVEIRA, Juliana Ferreira de; GOMES, Emerson Machi; ASCENÇÃO, Carolline Fernanda Rodrigues; HONORATO, Rodrigo; PAULETTI, Bianca Alves; INDOLFO, Nathalia de Carvalho; RIBEIRO FILHO, Helder Veras; OLIVEIRA, Paulo Sergio Lopes de; FIGUEIRA, Ana Carolina Migliorini; LEME, Adriana Franco Paes; AMBROSIO, André Luis Berteli; DIAS, Sandra Martha Gomes.},title={Glutaminase affects the transcriptional activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ? (PPAR?) via direct interaction},journal={Biochemistry},note={v. 57, n. 44, p. 6293-6307},year={2018}} @article={002912043,author = {CASSAGO, Carolina Aparecida de Guzzi; DIAS, Marília Meira; PINHEIRO, Matheus Pinto; PASQUALI, Camila Cristina; BASTOS, Alliny Cristiny Silva; ISLAM, Zeyaul; CONSONNI, Sílvio Roberto; OLIVEIRA, Juliana Ferreira de; GOMES, Emerson Machi; ASCENÇÃO, Carolline Fernanda Rodrigues; HONORATO, Rodrigo; PAULETTI, Bianca Alves; INDOLFO, Nathalia de Carvalho; RIBEIRO FILHO, Helder Veras; OLIVEIRA, Paulo Sergio Lopes de; FIGUEIRA, Ana Carolina Migliorini; LEME, Adriana Franco Paes; AMBROSIO, André Luis Berteli; DIAS, Sandra Martha Gomes.},title={Glutaminase affects the transcriptional activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ? (PPAR?) via direct interaction},journal={Biochemistry},note={v. 57, n. 44, p. 6293-6307},year={2018}} |



