Spin freezing in the disordered pyrochlore magnet NaCaCo2F7: NMR studies and Monte Carlo simulations.
SARKAR, R.; KRIZAN, J. W.; BRÜCKNER, F.; ANDRADE, Eric de Castro e; RACHEL, S.; VOJTA, M.; CAVA, R. J.; KLAUSS, H.-H.
SARKAR, R.; KRIZAN, J. W.; BRÜCKNER, F.; ANDRADE, Eric de Castro e; RACHEL, S.; VOJTA, M.; CAVA, R. J.; KLAUSS, H.-H.
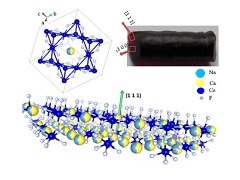 Abstract: We present results of 23Na and 19F nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements on NaCaCo2F7, a frustrated pyrochlore magnet with a Curie-Weiss temperature TCW = -140 K and intrinsic bond disorder. Below 3.6 K both the 23Na and 19F spectra broaden substantially in comparison to higher temperatures accompanied by a considerable reduction (80%) of the NMR signal intensity: This proves a broad quasistatic field distribution. The 19F spin-lattice relaxation rate 19(1/T1) exhibits a peak at 2.9 K already starting to develop below 10 K. We attribute the spin freezing to the presence of bond disorder. This is corroborated by large-scale Monte Carlo simulations of a classical bond-disordered XY model on the pyrochlore lattice. The low freezing temperature, together with the very short magnetic correlation length not captured by the simulations, suggests that quantum effects play a decisive role in NaCaCo2F7. Abstract: We present results of 23Na and 19F nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurements on NaCaCo2F7, a frustrated pyrochlore magnet with a Curie-Weiss temperature TCW = -140 K and intrinsic bond disorder. Below 3.6 K both the 23Na and 19F spectra broaden substantially in comparison to higher temperatures accompanied by a considerable reduction (80%) of the NMR signal intensity: This proves a broad quasistatic field distribution. The 19F spin-lattice relaxation rate 19(1/T1) exhibits a peak at 2.9 K already starting to develop below 10 K. We attribute the spin freezing to the presence of bond disorder. This is corroborated by large-scale Monte Carlo simulations of a classical bond-disordered XY model on the pyrochlore lattice. The low freezing temperature, together with the very short magnetic correlation length not captured by the simulations, suggests that quantum effects play a decisive role in NaCaCo2F7. | |
| Physical Review B |
| v. 96, n. 23, p. 235117-1-235117-10 - Ano: 2017 |
| Fator de Impacto: 3,836 |
| http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.96.235117 |  @article={002866435,author = {SARKAR, R.; KRIZAN, J. W.; BRÜCKNER, F.; ANDRADE, Eric de Castro e; RACHEL, S.; VOJTA, M.; CAVA, R. J.; KLAUSS, H.-H.},title={Spin freezing in the disordered pyrochlore magnet NaCaCo2F7: NMR studies and Monte Carlo simulations},journal={Physical Review B},note={v. 96, n. 23, p. 235117-1-235117-10},year={2017}} @article={002866435,author = {SARKAR, R.; KRIZAN, J. W.; BRÜCKNER, F.; ANDRADE, Eric de Castro e; RACHEL, S.; VOJTA, M.; CAVA, R. J.; KLAUSS, H.-H.},title={Spin freezing in the disordered pyrochlore magnet NaCaCo2F7: NMR studies and Monte Carlo simulations},journal={Physical Review B},note={v. 96, n. 23, p. 235117-1-235117-10},year={2017}} |



